peripheral nerve injury map
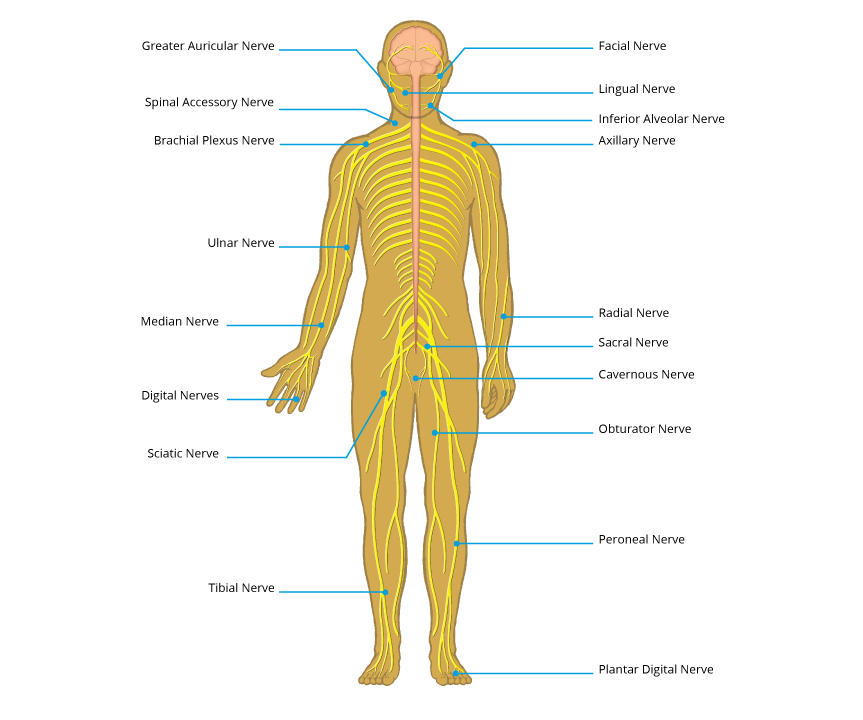
know your nerves
A peripheral nerve injury can occur anywhere in the body. Select an area of the body where you suspect nerve damage, and learn about those nerves, their functions, causes of injury, symptoms and treatments.
Head and neck
Greater auricular nerve
Provides sensations to the lower side of the face and ear
Common causes of injury:
- Unexpected injury during facelift procedures
- Surgical procedures such as removal of the parotid gland
- Use as a donor nerve for auto graft procedures
- Trauma such as a blow to the side of the head
Symptoms: Tingling, pain, and/or loss of feeling in the side of the face and ear.
Treatment: In the case of a nerve transection or neuroma, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair method can be used.
Inferior alveolar nerve
Provides sensation to the lower jaw, lip and teeth
Common causes of injury:
- Tooth extraction
- Jaw osteotomy, surgical realignment of the jaw
- Dental implant procedures
Symptoms: Tingling, pain, or loss of sensation in the lip and chin; may result in bite wounds or burn injuries of the lower lip.
Treatment: In the case of a nerve transection or neuroma, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair methods can be used.
Lingual nerve
Provides sensation to the tongue and the inside of the cheek
Common causes of injury:
- Tooth extraction
- Dental implant
- Anaesthetic injection
- Surgical procedures such as removal of a cyst or tumour
- Neuroma
Symptoms: Tingling, pain and/or loss of sensation in the inner mouth.
Treatment: In the case of a nerve transection or neuroma, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical methods can be used.
Spinal accessory nerve
Stabilises and shrugs the shoulder
Common causes of injury:
- Unexpected damage during surgical procedures
- Lymph node removal in the neck
- Radical neck dissection due to cancer
- Traumatic event such as a car accident
Symptoms: Slumping shoulder and pain in the upper back.
Treatment: In the case of a nerve transection or neuroma, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical methods can be used. For entrapment syndromes, doctors may prescribe pain and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce the pain as sometimes recovery happens on its own. In more serious cases, treatment requires decompression of the nerve. This procedure may require surgery to open the affected area and remove the compressing force on the nerve. In addition, specialised soft tissue implants may be used to wrap and protect the nerve from soft tissue attachments or to reduce inflammation.
Upper arm
Axillary nerve
Provides movement and sensation to the shoulder
Common causes of injury:
- Improper use of crutches
- Improper placement and tightness of a cast
- Traumatic event such as a car accident
- Fracture of the upper arm bone
Symptoms: Numbness or weakness in outer shoulder; inability to raise shoulder or lift objects.
Treatment: For a compression injury, a decompression surgery can be performed, which removes the pressure on the nerve. In the case of a nerve transection or neuroma, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair method can be used.
Brachial plexus nerves
Responsible for motor and sensory control of the hand, wrist, elbow and shoulder
Common causes of injury:
- Traumatic event such as a car accident
- Erb’s palsy (damage during childbirth)
Symptoms: Limp arm and loss of sensation in the shoulder, arm and hand; may be unable to lift arm or flex at the elbow; weakness, pain or numbness may also occur; severe cases may cause complete arm paralysis.
Treatment: In the case of a nerve transection, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair method can be used.
Pelvis
Cavernous nerve
Facilitates penile erection and urinary continence
Common causes of injury:
- Prostatectomy, removal of the prostate
- Colorectal surgery
Symptoms: Erectile dysfunction or urinary incontinence.
Treatment: In the case of a nerve transection, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair methods can be used. Grafting procedures of the cavernous nerve are typically done robotically.
Lower arm and hand
Ulnar nerve
Allows movement and sensation in the wrist and hand
Common causes of injury:
- Entrapment of the nerve
- Traumatic event such as a car accident
- Neuroma
Symptoms: Numbness, pain or weakness in the hand; loss of coordination of the fingers and weakness of hand flexing.
Treatment: The treatment for entrapment syndromes consists of removing the compressive pressure on the nerve. Surgery is often needed to free the nerve, and a protective wrap can be placed around the nerve to help minimise the compressive pressure. In the case of a nerve transection or neuroma, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair methods can be used.
Median nerve
Controls movement and sensations in the hand
Common causes of injury:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Laceration
- Traumatic event such as a car accident
- Neuroma
Symptoms: Loss of sensation, pain, and/or inability to move the forearm, wrist, or hand; inability to hold objects with the hand.
Treatment: Treatment is specialised to correct the underlying cause. For entrapment syndromes, a splint may be worn at night to allow inflammation to decrease, and sometimes recovery happens on its own. In more serious cases, treatment requires decompression of the nerve. This procedure may require surgery to open the affected area and remove the compressing force on the nerve. In addition, specialised soft tissue implants may be used to wrap and protect the nerve from soft tissue attachments or to reduce inflammation. In the case of a nerve transection or neuroma, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair methods can be used.
Radial nerve
Controls sensations of the back of the hand and wrist, and controls the finger-thumb pinch motion
Common causes of injury:
- Entrapment of the nerve
- Traumatic event such as a car accident
- Result from humeral breaks or fractures
- Neuroma
Symptoms: Numbness/tingling or weakness in the wrist, fingers and thumb; may cause wrist drop.
Treatment: The treatment for entrapment consists of removing the compressive pressure on the nerve. Surgery is often needed to properly free the nerve, and a protective wrap can be placed around the nerve to help minimise the compressive pressure or reduce inflammation. In the case of a nerve transection or neuroma, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair methods can be used.
Digital nerve
Provides sensation to the fingers
Common causes of injury:
- Laceration
- Traumatic event such as a power tool accident
Symptoms: Tingling, pain and/or numbness.
Treatment: In the case of a nerve transection, direct repair, auto graft, allograft, hollow tube conduit or other surgical repair methods can be used.
Upper leg
Obturator nerve
Provides motor and sensory function to the thigh
Common causes of injury:
- Pelvic or abdominal surgery
- Entrapment of nerve
Symptoms: Loss of sensation in thigh; inability to pull leg into the body.
Treatment: In the case of a nerve transection, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair methods can be used. Treatment for compression injuries can include pain medications and physical therapy. If problems persist, surgery might be necessary to remove the compressive pressure on the nerve.
Sacral nerve
Innervates buttocks and thigh and helps control urinary and faecal excretion
Common causes of injury:
- Traumatic events such as serious falls
- Vaginal childbirth
- Hysterectomy
- Surgical removal of tumours
Symptoms: Muscle weakness and/or shooting, burning, or stabbing pain running from buttocks to thigh; potential problems with urination and/or defecation.
Treatment: Depending on the injury type, the patient may be treated using physical therapy, steroids and pain medication. If these do not work, surgery may be an option.
Sciatic nerve
Provides sensation and movement to the back of thigh, leg and foot
Common causes of injury:
- Traumatic event such as an ATV accident
- Hip implant surgeries
Symptoms: Pain, weakness and/or numbness down the back of the leg to the knee; loss of sensation below the knee.
Treatment: For traumatic injuries and injuries caused by hip implant surgeries that lead to a transection of the nerve, surgical methods are needed for proper nerve repair. These methods could consist of a direct repair, an auto graft or an allograft, among other choices. Compression of the nerve either by traumatic event or the placement of a hip implant can be treated by removing the compressive pressure on the nerve. To aid in the repair of the nerve, a protective wrap can be placed around the nerve to help minimise the compressive pressure or reduce inflammation.
Lower leg
Peroneal nerve
Controls movement and sensation to the lower leg, foot and toes
Common causes of injury:
- Traumatic event such as a car accident
- Compression of nerve in fibular tunnel
- Knee injuries
Symptoms: Inability to hold foot horizontal (foot drop), weakness and/or loss of sensation in ankle and foot, or walking abnormalities.
Treatment: Therapy, steroids and time might be enough to allow function to return. In the case of a nerve transection or neuroma, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair methods can be used. For entrapment syndromes, doctors may prescribe pain and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce the pain caused as sometimes recovery happens on its own. In more serious cases, treatment requires decompression of the nerve. This procedure may require surgery to open the affected area and remove the compressing force on the nerve. In addition, specialised soft tissue implants may be used to wrap and protect the nerve from soft tissue attachments or to reduce inflammation.
Plantar digital nerve
Provides sensation to the toes
Common causes of injury:
- Traumatic event
- Morton’s neuroma
Symptoms: Pain or tingling between the toes and on the ball of the foot, or the sensation of walking on a marble.
Treatment: Doctors normally take a very conservative approach with this injury and prescribe pain and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce the pain caused by the injury. In the case of a nerve transection or neuroma, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair methods can be used.
Tibial nerve
Provides movement and sensation to the calf and foot muscles
Common causes of injury:
- Traumatic event such as a car accident
- Fractures located in the back of the knee or lower leg
- Neuroma
Symptoms: Loss of function or sensation in the lower leg, specifically in the calf and foot.
Treatment: In the case of a nerve transection or neuroma, direct repair, auto graft, allograft or other surgical repair methods can be used. For entrapment syndromes, doctors may prescribe pain and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce the pain as sometimes recovery happens on its own. In more serious cases, treatment requires decompression of the nerve. This procedure may require surgery to open the affected area and remove the compressing force on the nerve. In addition, specialised soft tissue implants may be used to wrap and protect the nerve from soft tissue attachments or to reduce inflammation.
